Overview of Tropical Storm Beryl: Tropical Storm Beryl Spaghetti Models
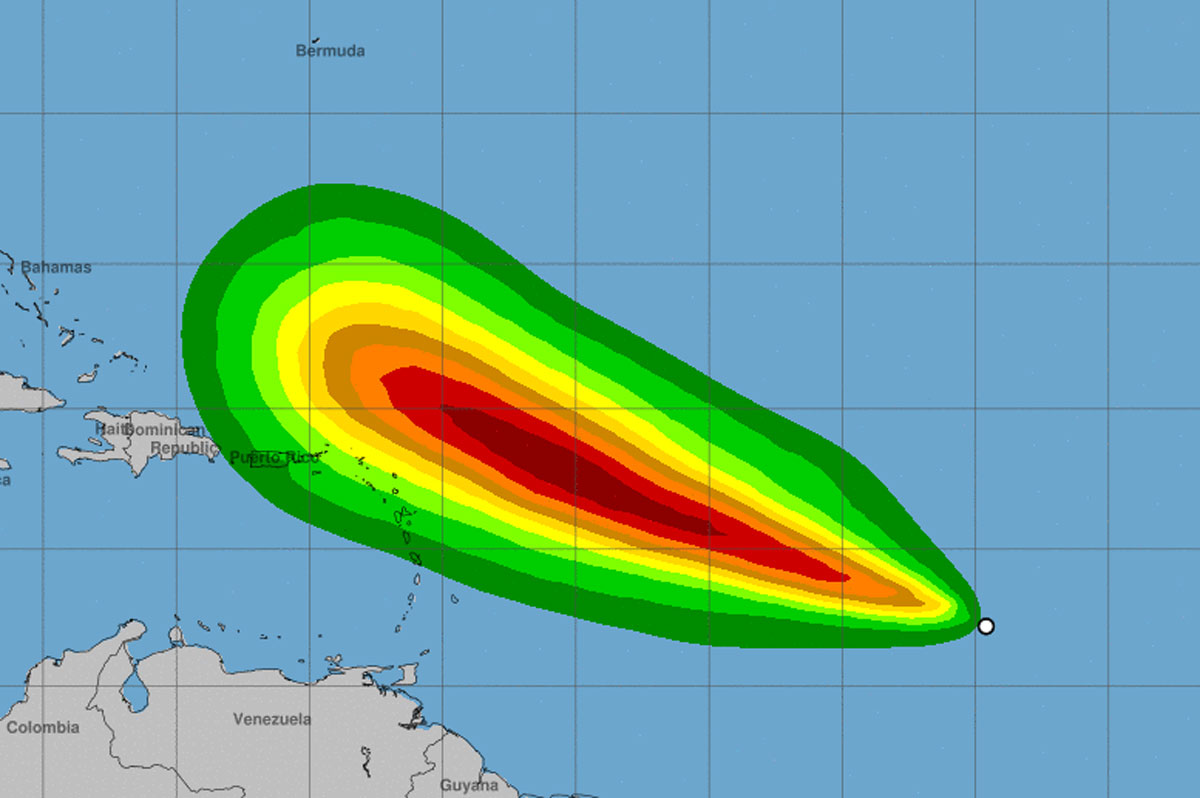
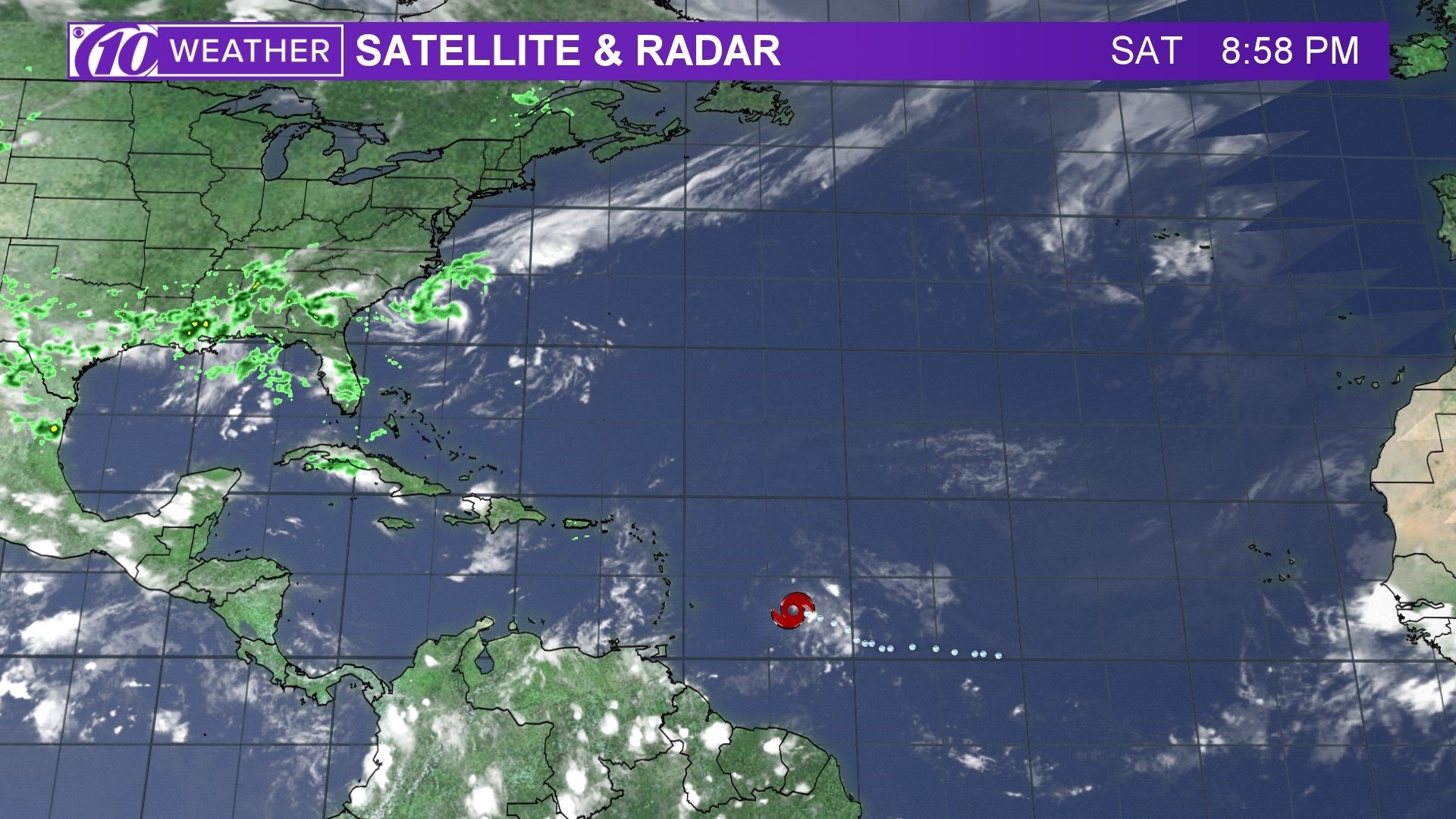
Tropical storm beryl spaghetti models – Tropical Storm Beryl emerged as a tropical depression on July 10, 2023, and has since intensified into a tropical storm. It is currently located approximately 1,200 miles east of the Lesser Antilles, with maximum sustained winds of 40 miles per hour.
The National Hurricane Center has issued tropical storm warnings for Barbados, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada. Tropical storm watches are in effect for Dominica, Martinique, and Guadeloupe.
Projected Path, Tropical storm beryl spaghetti models
The projected path of Tropical Storm Beryl is expected to take it across the Lesser Antilles on Tuesday and Wednesday. The storm is then forecast to turn northwest and move towards the Bahamas and Florida by the end of the week.
Potential Impact
Tropical Storm Beryl is expected to bring heavy rainfall, strong winds, and possible flooding to the Lesser Antilles. The storm could also cause power outages and damage to infrastructure.
Analysis of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models, also known as ensemble models, are a collection of individual computer model runs that simulate the potential path of a tropical storm. Each model run uses slightly different initial conditions and/or model physics, resulting in a range of possible tracks.
Spaghetti models provide valuable insights into the uncertainty associated with tropical storm forecasting. By examining the spread of the model tracks, meteorologists can estimate the likelihood of different scenarios and identify areas that are most at risk.
Types of Spaghetti Models
There are several different types of spaghetti models available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
- Global Forecast System (GFS): The GFS is a global weather model that is run four times per day. It is one of the most widely used spaghetti models and is known for its accuracy in predicting the general track of tropical storms.
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): The ECMWF is a European weather model that is run twice per day. It is known for its skill in predicting the intensity of tropical storms.
- Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting (HWRF): The HWRF is a hurricane-specific model that is run twice per day. It is known for its ability to predict the rapid intensification of tropical storms.
Interpreting Spaghetti Models
To interpret spaghetti models, meteorologists look at the spread of the model tracks. A tight spread indicates that the models are in good agreement about the storm’s track, while a wide spread indicates that there is more uncertainty.
Meteorologists also consider the track of the individual model runs. A model run that consistently predicts a different track than the other models may be an outlier and should be given less weight.
By combining the information from the spaghetti models, meteorologists can develop a consensus forecast track for the tropical storm. This forecast track is not a guarantee, but it provides valuable information about the storm’s most likely path.
Ah ha! We see you be lookin’ for tropical storm beryl spaghetti models, yeah? You want to know where it be headin’, right? Well, let us tell you ’bout spaghetti models. These here models be like a bunch of noodles, showin’ you all the possible paths that storm could take.
So, you can see where it might be goin’ and make your plans accordingly. Now, let’s get back to them tropical storm beryl spaghetti models, yeah?
Tropical storm Beryl spaghetti models predict a possible landfall in Florida. For the latest updates, visit the nhc beryl website. Spaghetti models are computer simulations that show the potential paths of a storm, and they can be helpful in determining the likelihood of a landfall.